With the adoption of Cloud services, the Internet with SD WAN is now viewed as a cost-effective, agile alternative to MPLS VPN. In today’s world of cloud-based applications, the question on the mind of most IT teams surrounds whether or not MPLS is required vs using an Internet connection as the basis of your SD WAN underlay.
Which WAN is better for your Enterprise, MPLS or SD WAN?
The answer in the majority of cases is SD WAN. In reality, larger Enterprise businesses often end up with a hybrid of services which include SD WAN, layer 3 MPLS, layer 2 VPLS and SHDS (Short Haul Data Services).
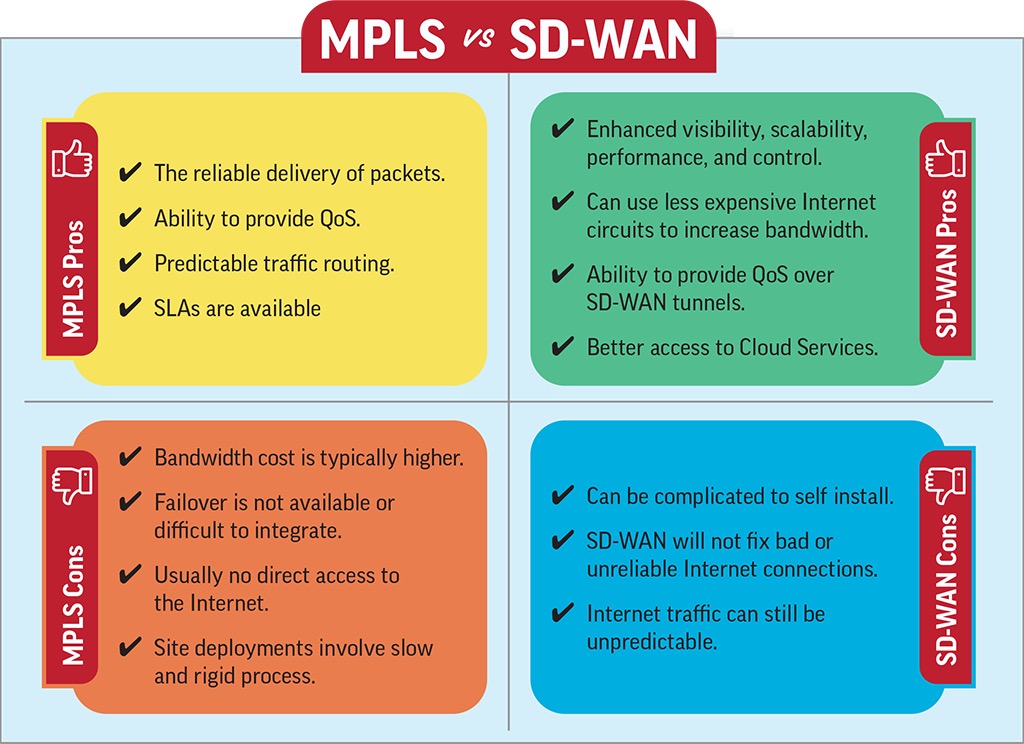
What are the benefits and pros of SD WAN solutions?
- The ability to leverage any Internet connection based on the location
- Access to public cloud applications across desktop, laptop, mobile and tablet devices
- Easy orchestration with capability to virtualise SD WAN or use traditional edge CPE
- Fast deployment with less reliance on lengthy delivery of MPLS circuits
- Delivery of SD WAN is made more accessible via automated orchestration with zero-touch deployment
- SASE and/or next generation Firewall security
- Wider range of connectivity including 4G, 5G and Broadband Internet
- The overall value revolves around the flexibility and agility of software development API’s, which exist within a central management server.
- SD WAN services offer firewall level packet inspection for security, reporting, and traffic prioritisation with real-time sensing of network performance.
- An Internet circuit generally represents a lower cost vs. MPLS; these cost savings are driving interest in SD WAN services.
- Software WAN is deployed with traditional WAN edge or virtualised instances.
- SD WAN feature sets can improve network connectivity performance, including the average low cost broadband connection.
What are the benefits and pros of MPLS solutions?
- MPLS NOC teams typically offer good support for customers with highly focussed knowledge of their customer base
- Managed services are highly focussed with teams possessing years of experience supporting customers
- End to end support for applications across EF (Expedited Forwarding for delay sensitive apps), AF (Assured Forwarding for mission critical applications) and Be (Best Effort for all other traffic)
- Inherent privacy with no requirement for additional security and encryption via IPSec (not recommended)
- MPLS traffic prioritisation is end-to-end but local; the core internet does not care about the priority of your IP packets
What are the use cases – how to compare SD WAN vs. MPLS?
SD WAN offers huge agility and flexibility by leveraging highly effective feature-sets which include:
- WAN link-aggregation
- Application acceleration
- Next-Generation Firewall (NGF)
- Security
- Comprehensive statistics
- Access to cloud providers
- Secure connections from multiple hosts (depending on vendor)
- Diversity & redundancy using multiple paths
The key driver behind SD WAN adoption is the use of public cloud applications and the need for users to connect over the Internet from HQ, branch office and from any remote location. MPLS does not meet the needs of todays hyper connected business and is therefore in decline. With this said, where the architecture requires connecting offices together for data transfer only, MPLS remains a viable option as does VPLS and private circuits.
Is MPLS more secure than SD WAN?
No. Although MPLS circuits are private and theoretically do not require additional security, the threats which exist today mean that SD WAN with SASE and next generation security is more secure. While every writer has their own opinion on this point, we would no longer deploy MPLS without some form of additional security layer. And, if you buy into the need for additional security, why bother with MPLS at all unless there is a specific need as mentioned earlier?
SD WAN with SASE security adds IPS (Intrusion Protection), next generation Firewall (FWaaS – Firewall as a Service), SWG (Secure Web Gateway), ZTNA (Zero Trust network access). All of these afore mentioned features are needed to secure users regardless of whether MPLS or SD WAN over the Internet is deployed.
Does SD WAN work over MPLS?
Yes, but some vendors offer better support for MPLS. As an example, Meraki does support MPLS provision but the technology is not a natural fit due to the way in which VPN tunnels are deployed. The majority of SD WAN vendors will support hybrid services but we would advise checking prior to engaging with sales.
Do some SD WAN vendors offer private MPLS core access?
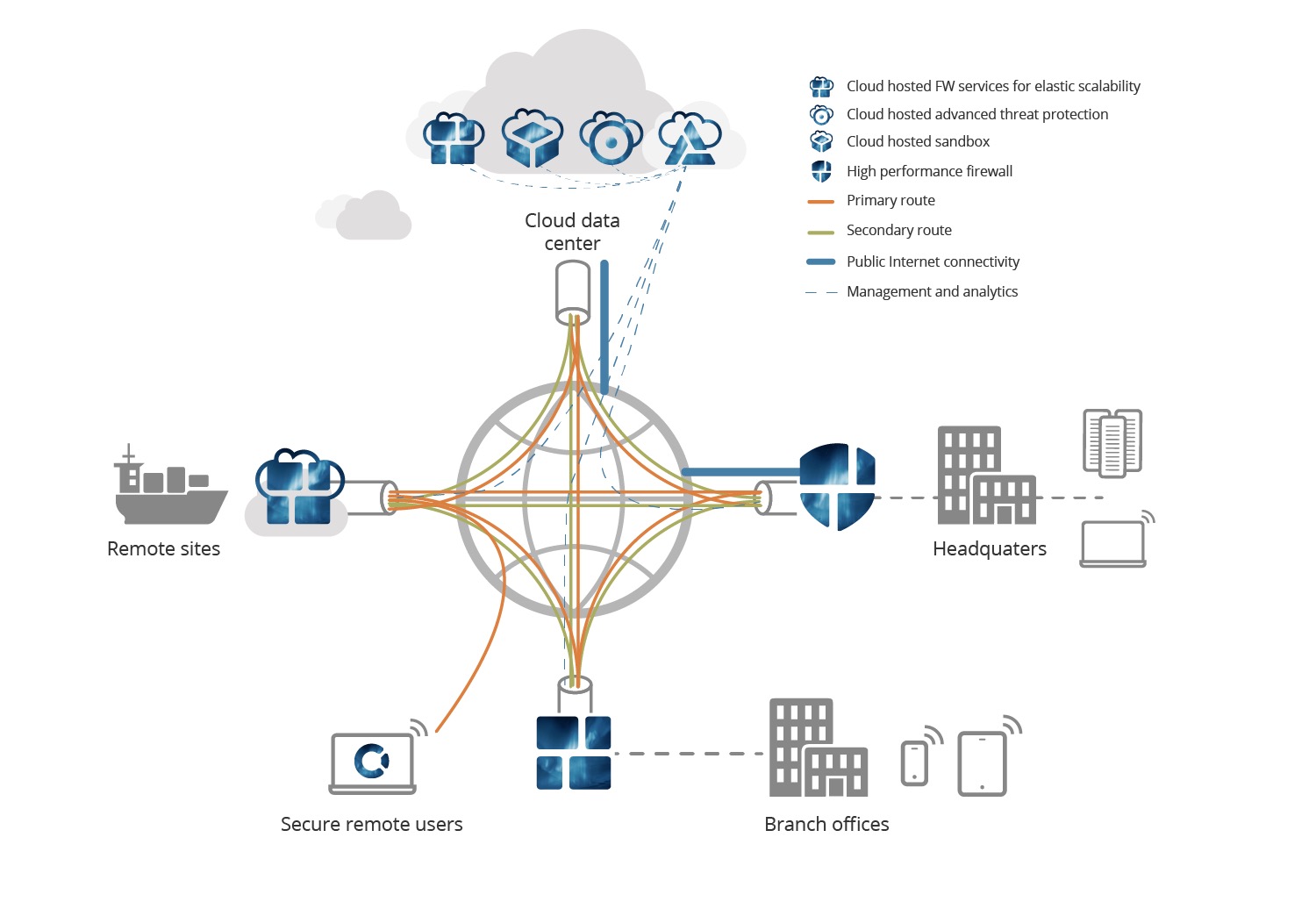
Yes, there are a number of SD WAN vendors which operate private and public networks for Global customers. Customers connect into the nearest private PoP location via VPN, traffic is then transported across the vendors private backbone. In many ways, vendors with private backbones are essentially offering the best of SD WAN and MPLS.
In addition to private PoPs, vendors are also providing access to pubic gateways which are interconnected via multiple ISP services. The corporate VPN traffic is directed over the most optimum route depending on destination or cloud service (e.g. Azure or AWS).
The value behind an SD WAN vendor with private backbone surrounds the local Internet access which can be configured via split tunnelling at the branch/user level or via the local cloud node. The SD WAN vendor PoP offers Internet access with cloud optimisation and transport of traffic to other PoP’s on a global basis. Global enterprise businesses considering SD WAN should use a single public IP backbone for the main offices and branch locations to ensure good latency and jitter for both delay-sensitive and mission-critical applications.
How does SD WAN Qos compare with MPLS QoS?
MPLS QoS is one of the key adoption reasons for Enterprises needing to offer their users guaranteed traffic performance across latency and jitter on an end to end basis. While SD WAN over the Internet cannot guarantee performance end to end, the control of traffic is much more granular together with an ability to sense performance degradation and re-route traffic accordingly. And, some vendors offer FEC (Forward Error Correction) to further improve resilience against issues.
It is also the case that MPLS VPN QoS cannot be configured on a dynamic basis which means that the values must be correct to make the most of the capability. In the majority of cases, MPLS bandwidth values are often set correctly which results in detrimental network performance.
With the adoption of Cloud services, the Internet with SD WAN is now viewed as a cost-effective, agile alternative to MPLS VPN. In today’s world of cloud-based applications, the question on the mind of most IT teams surrounds whether or not MPLS is required vs using an Internet connection as the basis of your SD WAN underlay.
And a key critical consideration, can your organisation migrate existing MPLS circuits over an SD WAN based environment if the WAN is operating within an existing service provider contract.
In the main, the following 3 areas are the most common considerations for IT teams:
- The requirement to make use of MPLS circuits currently in contract alongside new Internet based SD WAN deployments.
- The business mandates end to end QoS with inherent privacy – which SD WAN vendors support MPLS?
- There is a need to evaluate MPLS vs SD WAN solutions due to the end of an existing contract.
Is there an absolute need for MPLS?
At a high level, the answer revolves around business requirements for data centre, HQ and branch office locations. The reduction in MPLS deployments is occurring across service providers; we are experiencing MPLS replacement projects with our own Netify clients.
Let’s look at the top reasons why IT teams are moving to SD WAN
- Cost savings
- Business agility
- Additional bandwidth
- Cloud access
- Next generation Firewall & SASE security
- Application sensing
- Comprehensive statistics
Let’s look at the top reasons why IT teams are staying with MPLS
- End to End QoS
- NOC support is typically better vs Internet
- Network privacy
- Comprehensive SLA (Service Level Agreement)
If we, as IT professionals, conceptually consider MPLS vs Internet in isolation, there remains no better way to transport international traffic with the best possible performance guarantees across latency, jitter, packet loss and uptime.
“If we, as IT professionals, conceptually consider MPLS vs Internet in isolation, there remains no better way to transport international traffic with the best possible performance guarantees across latency, jitter, packet loss and uptime.”
MPLS remains a good solution under certain circumstances depending on business requirements.
With this said, this last statement could be construed as a little misleading, especially if you’re an IT Manager or IT Director involved in Software-WAN vendor evaluation.
The reason for thinking the statement might be misleading surrounds the SD WAN features mentioned earlier which include bandwidth aggregation, real-time WAN link monitoring and specific application treatment in the event your primary WAN connection is lost. In this respect, MPLS (in traditional WAN edge form) does not offer comparable features.
Understand the benefits SD WAN brings to your business
IT teams need to consider why your business may want to retain or procure new MPLS circuits rather than adopt Internet connectivity. If we view MPLS on a whiteboard, or any kind of technical presentation, the benefits stand out as fairly obvious.
These obvious features explain why the market has witnessed such growth over the decades. Why wouldn’t an Enterprise require end to end QoS, privacy and robust business guarantees?
Here’s one reason why MPLS may not be as valuable today vs the past. While end to end QoS is a benefit, customer application traffic is no longer easily categorised with the advent of multiple cloud-based services. In this respect, Netify is working with clients that have removed QoS from their network due to detrimental performance of other traffic types. In other words, businesses no longer wish to offer sub-standard performance regardless of the application type, i.e. best effort or even assured forwarding (AF).
As the WAN environment becomes more complex, creating QoS policies and categorising applications is becoming increasingly difficult. SD WAN technology offers the necessary statistics to help build these policies. The question remains, is it possible to categorise every application and prioritise above general Internet access which may be deemed as equally important.
Does SD WAN over MPLS create the best possible value proposition?
On the whole, there is a strategy shift from deploying traditional Cisco style WAN edge devices with static QoS policies to combining MPLS circuits over Software-WAN. Whether or not this strategy will work well for your organisation is dependent on the capability of the SD WAN solution vendor to offer up data statistics needed to add QoS policies effectively.
Where your business is required to make use of existing MPLS, or perhaps the business mandates the privacy of MPLS, using SD WAN can replace QoS with other features suited for internet traffic. SD WAN solutions with FEC (Forward Error Correction) and packet duplication are highly effective methods of ensuring voice quality without actual end to end traffic policing.
Your business could consider using MPLS as a primary circuit together with an Internet-based secondary with Software-WAN features. While your voice traffic may not be categorised in respect of QoS bandwidth end to end (on the failover), the ability for SD WAN to duplicate packets means if the MPLS primary fails, or suffers congestion or packet loss, the secondary circuit is utilised. I.e. voice packet duplication means there is a constant second ‘recording’.
Features such as FEC with packet duplication, WAN aggregation, WAN optimisation and Next-Generation Firewall Security are the very reason why MPLS is perhaps not as effective as we believe when evaluating and comparing WAN services. While QoS was the main WAN service provider feature over recent years, SD WAN over the Internet offers an alternative feature set to relegate MPLS into the past.
What if your business must keep MPLS due to contractual commitments?
Certain vendors will support MPLS circuits as a component of hybrid connectivity. We would note that the majority of SD WAN solutions do not consider MPLS VPN services as a component of Software Defined strategy. There are currently vendors offering to remove the MPLS provider costs during migration to assist with the move from MPLS to an Internet-based solution. (Learn more about this by completing a Netify SD WAN comparison)
Is MPLS (Multi-Protocol Label Switching) an important component of hybrid WAN architecture as the Enterprise adopts SD WAN technology?
The core value of software WAN services surrounds the innovation surrounding capability. The goal of SD-WAN is to ultimately deliver hardware that is configured via a software-based central management server. The traditional approach of deploying features is via regular software updates; security and additional features are added over time.
With software WAN, developers (as a high level) are positioned to explicitly write a feature or capability as they would any application. The result is a much quicker, focused approach to WAN enhancements.
QoS over MPLS vs Internet based SD WAN underlay
- QoS (Quality of Service) MPLS WAN offers end-to-end prioritisation of application traffic, typically over six settings.
- SD WAN services provide more granular control of application traffic, but not end-to-end.
- MPLS QoS is relatively simple to understand. The process is to mark traffic with a setting (i.e., DSCP) which is followed end-to-end, ideal for critical applications.
Above, you’ll see traffic marked at the customer edge through to the provider edge and core provider device. This approach allows organisations to be confident in the performance of their applications, even under congestion. SD WAN is somewhat different. At first glance, traffic prioritisation is achieved by analysis of applications to a much more detailed level vs. MPLS QoS.
SD software analyses traffic and gauges end-to-end path performance. The ability to consider the end-to-end path is how SD WAN achieves an experience comparable to MPLS. With this in mind, the analysis of your internet connectivity must be carefully considered during the procurement process. SD WAN functionality is available on multiple devices, including software-based clients.
This aspect provides a standardised set of security policies via one vendor across all of your user and extranet profiles offering a huge benefit as you deploy corporate resources with security and application performance enhancements. Couple these advantages with a lower cost of connectivity vs. MPLS, and you’ll quickly understand why SD WAN is growing in popularity.
Cloud Services are driving the take up of SD WAN The majority of resources employees use today are using cloud-based applications via Microsoft Azure, AWS and Google Cloud. These hosted apps include video conferencing, voice, instant messaging, file storage and backup.
Finally, with an SD WAN solution, you’re leveraging on the power of the Internet, including mobile 4G/5G access, Internet leased lines and broadband access to cloud resources. In other words, users can work from wherever they are located. Offering a comparable experience across MPLS networks requires a connection with cloud providers or the creation of a private cloud. Remote users will need some form of gateway with VPN (Cisco DM VPN as an example) to secure connectivity in the office.